Technology
When using perforated air-duct technology, the ventilation system provides for air circulation through produce piles with the aid of floor-mounted ducts, creates uniform temperature and moisture throughout the produce and displaces excessive levels of carbon dioxide and the other byproducts generated when vegetables breathe the fresh air.
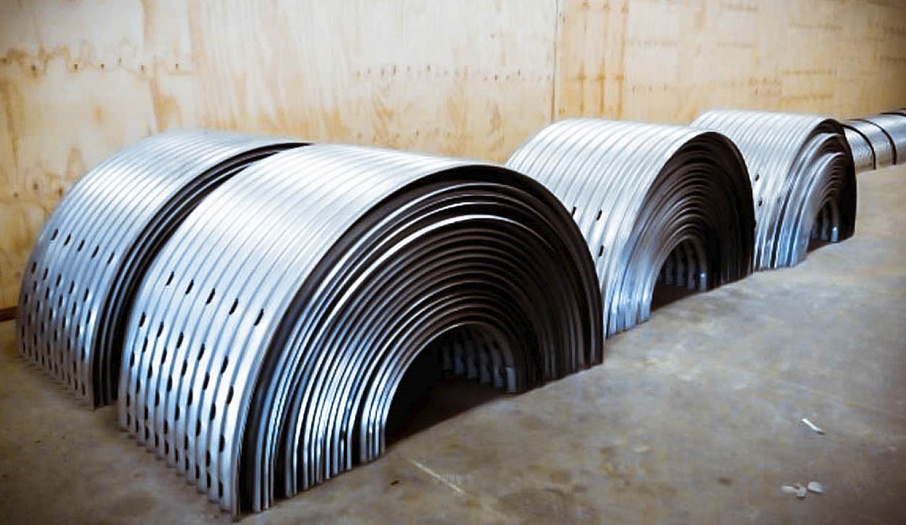
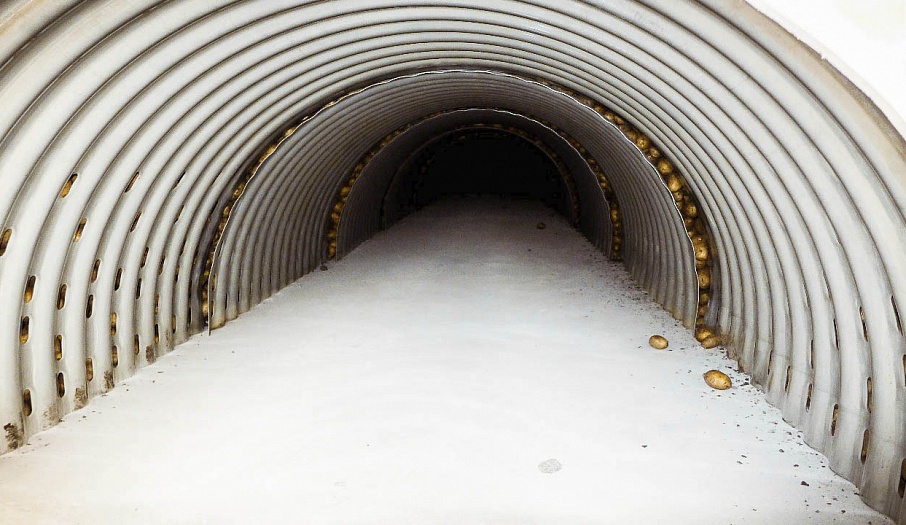
Perforated air ducts
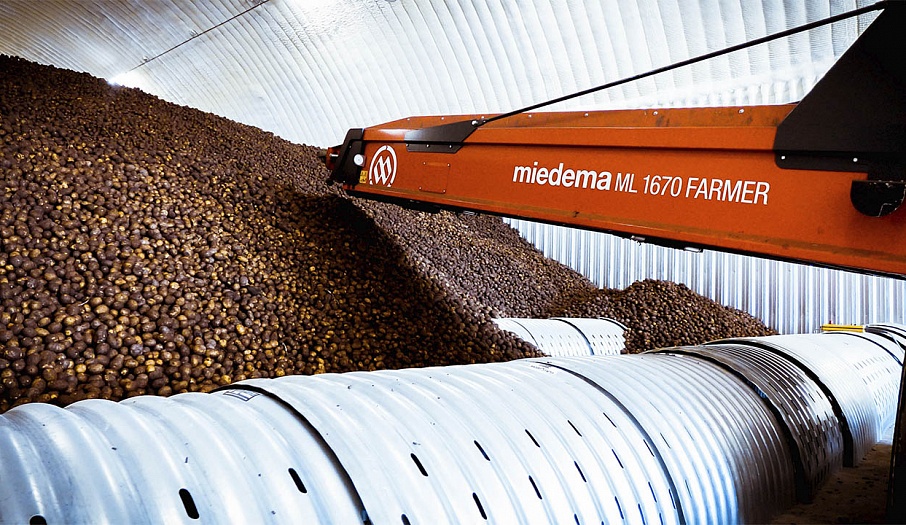
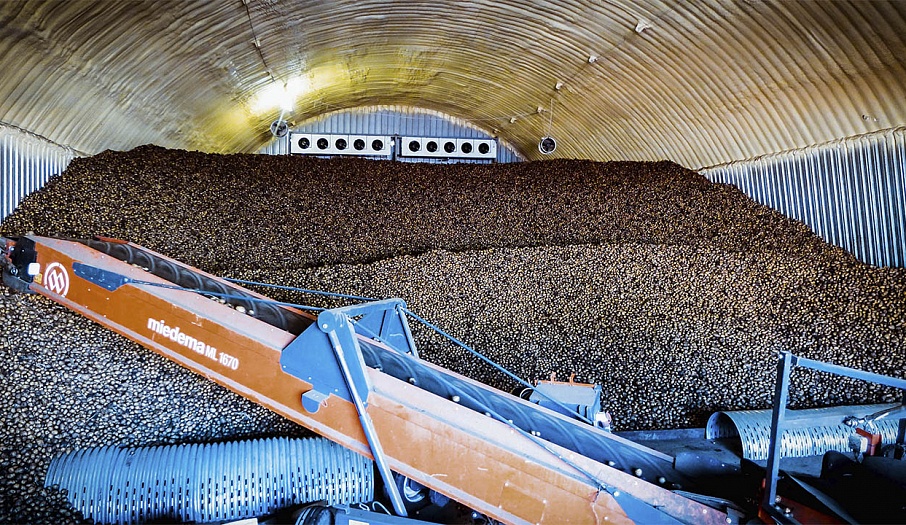
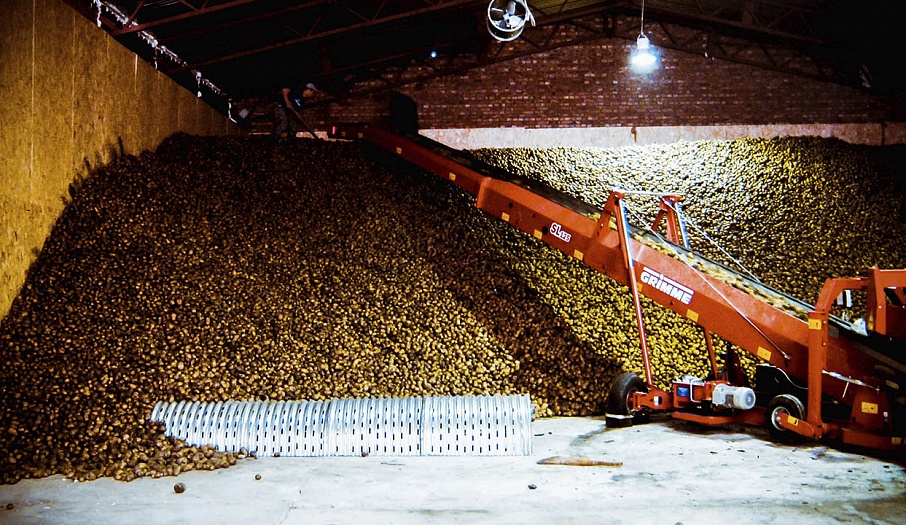
Storing produce in bulk on the floor of the facility is one of the most common storage methods in Russia. The popularity of opting for this storage method is explained by its many advantages, such as: efficient use of storage capacity, optimal ventilation and drying throughout the mass of produce, even temperature maintenance and lack of necessity for wooden containers. This type of storage is the most common on the industrial scale.
.png)
Bulk storage is perfect for potatoes, onions and beets. The ventilation system consists of a load-bearing wall (air-ventilation chamber), the walls of the vegetable storage building and floor-mounted air ducts. The fresh air flows through the intake valves on the load-bearing wall into a mixing chamber where it mixes with the recirculated air from the storage, obtains the required temperature and humidity levels, and is delivered to the bulk of produce through the floor-mounted air ducts.
The ventilation system is fundamental and is used for drying, curing, decreasing and maintaining the temperature of produce.
The temperature and humidity of the incoming air can be regulated with the use of the recycle valves, humidifiers, heaters and coolers, which are also located in the storage. Forced-air fans can be installed either directly in each floor duct or on the hollow floor in the air-preparation chamber. In arched hangars, fans are installed in a specific-capacity grouping at the abutting end of the hangar. The prepared air is delivered into the zinc-plated floor-mounted air ducts with the help of high-pressure forced-air fans through the main level ducts. Depending on storage mode, when the air goes through a pile, it ventilates, cools or dries the produce. If needed, a particular duct can be closed off; for example, if some of the produce in storage has already been shipped, or if a high volume of air needs to be supplied to just-stored produce that has recently been damp.
Forced by the high-pressure fans, waste air is removed though the open exhaust valves, or is mixed with the fresh incoming air through the recycle valves. The cycle repeats.
In order to prevent the formation of condensation in a vegetable storage, special fans are suspended at specific intervals (some of which are equipped with heating elements).
For automatic microclimate maintenance in a storage, a Croptimiz-R controller is used. The controller is equipped with produce-temperature sensors, outer and inner sensors for temperature and humidity, and a sensor for carbon-dioxide concentration (CO2). The dispatch system makes it possible to adjust and monitor the microclimate conditions in a storage building by using a computer or smartphone.
The independent system for the removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) maintains the required concentration of carbon dioxide in the chamber to avoid produce rot as a result of high CO2 concentration.
The air is collected and removed from the storage through the bottom part from the chamber. If the CO2 sensor indicates a dangerous (pre-set) gas concentration, the controller switches on the removal system automatically.
This system makes it possible to avoid exceeding the pre-set CO2 concentration and using the main forced-blowing system, which can lead to microclimate deviations and extra power consumption.
A refrigeration system is used at high outside temperatures (in April, May, June).
Refrigeration
Mechanical air cooling in a storage using a refrigeration system is designed in such a way so as to avoid impacting produce quality and minimize produce crusting and drying.
For this purpose, the system uses air coolers that have been specially designed for the storage of fruits and vegetables. They feature an enlarged heat-exchange finning surface and low air consumption, an enlarged fin pitch and “corridor” pipe pitch in the cooler housing, thereby achieving the lowest-possible “temperature drag.”
The specific arrangement of fans near the entrance to the air cooler provides the air drag into the heat exchanger of the air cooler (forced air coolers), which decreases condensate falling onto the surface of the produce and lowers the rate of produce drying.
These ducts have laminar airflow with a low speed. It is extremely important that the minimum temperature drop should be less than 6 degrees (Dt6k), which means that the boiling temperature of freon gas should be 6 degrees lower than the temperature in the chamber. Flow control of freon and accurate mode maintenance is provided with an electronic regulating valve (thermal expansion valve).
Automation
The required storage parameters are maintained with an automatic control system, which was specially designed for vegetable storages.
It provides for the:
- Control of storage modes;
- Control of the refrigeration system;
- Control of the humidification system;
- Control of drying modes;
- Data collection and archiving;
- Monitoring and remote control.
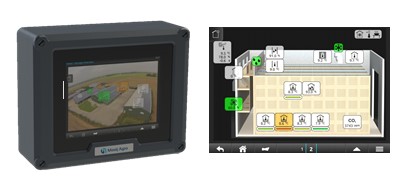
The information can be automatically sent from the storage controller to a profile page or smartphone, where the user can review, organize and archive the relevant data.
Completed projects
more Region: Prudischi Village, Venevsky District, Tula Region
Client: “Bykov” Family Farm
more Region: Spitsyno Village, Shatrovsky District, Kurgan Region
Client: “Grekhov” Family Farm
more Region: Achairsky Village, Omsk District, Omsk Region
Client: “SN-Agro”
more Region: Levashovo Village, Nekrasovsky District, Yaroslavl Region
Client: “Kommunar” SK
Blog
Storage technology
Rectangular building conveniently
Reconstruction building
Bulk storage




