Vegetable storage technology
08.05.2018 | Storage technology
In order to choose a suitable vegetable storage technology, you need to take into account lots of factors such as financial resources, produce type and size.
There are two types of storing vegetables. They are bulk and container storage.
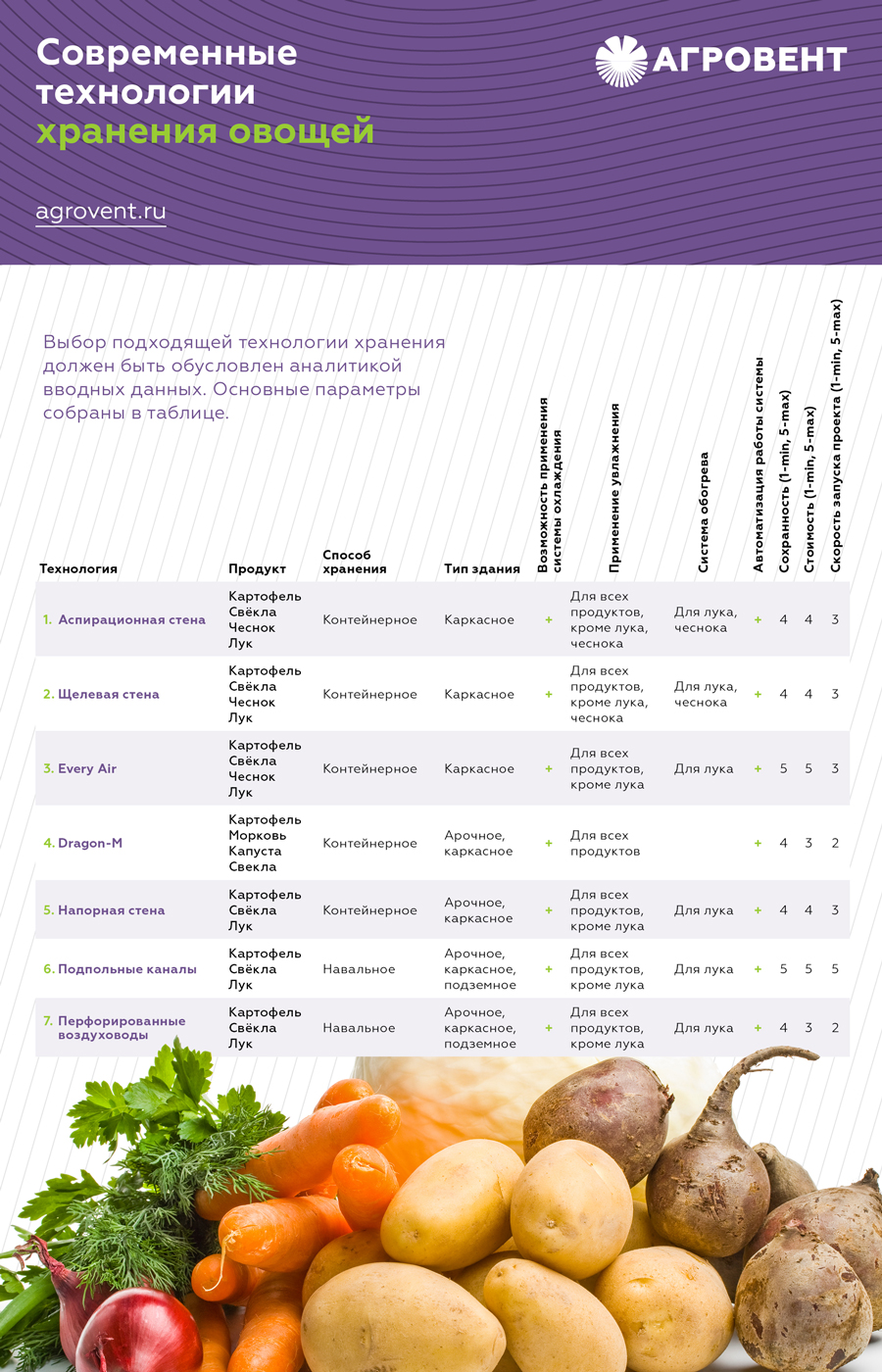
Bulk storage
This type of storage is the most common in Russia. It allows for storing a big amount of produce. It is suitable for storing onions, potatoes and beets.
The air preparation chamber in a vegetable storage under the bulk storage technique is important for maintaining climate index. It is better to locate the chamber along one of the outer walls of the vegetable storage building and to separate it from the inner wall of the storage room. Fresh air passes into the chamber through the intake valves, where it gets the required level of humidity and temperature. The recycle valves, heaters, humidifiers and coolers located in a chamber are used for maintaining the air that comes into the chamber.
Bulk storage with underfloor ducts entails the supply of air prepared with the help of high-pressure fans, where the air runs through the special cement underfloor ducts. Fans can be installed into the hollow floor of the air preparation chamber or into ducts. The air passes through the ducts and into the storage where it ventilates, heats or cools the vegetables. It also adjusts humidity. After that, the waste air mixes with the fresh air through the recycle valves or through the open intake valves. In order to avoid the formation of condensate, the storage rooms are equipped with special fans, which can be fitted with heating elements.
The automatic control system is used in a storage for maintaining the required microclimate parameters; it is operated with a computer with the aid of produce temperature sensors and ducts, inner and outer humidity sensors, and controls the microclimate inside the storage building.
Bulk storage with perforated air circuits is necessary if installing underfloor ducts for airflow is not an option. For example, if you’re trying to equip a ready-built storage facility. A perforated metal air circuit is installed on the level floor. The prepared air moves away from the chamber through the air circuits and then comes out through the slots in the ducts and passes through the produce.
Underfloor ducts can be installed in any existing vegetable storage if minor modifications are made. This vegetable storage option is the fastest and the cheapest. At the same time, it means losing a certain percentage of storage capacity. Our specialists have estimated that perforated air circuits take up approximately 7% of total room space. Another disadvantage is the inconvenience of cargo operations by electric lift trucks and the other equipment typically used in a storage. Ducts can get damaged by such equipment, meaning that they will have to be replaced from time to time. On average, about 10% of air circuits are replaced every year. At the same time, storage quality with perforated air circuits is similar to the quality provided by underfloor ducts.
Container storage
Container storage guarantees a high level of crop safekeeping. The process of maintaining produce quality is convenient and allows for the prompt removal of spoiled vegetables, provides for the convenient loading and unloading of produce and a high degree of process mechanization, and makes it possible to store different types of vegetables in a single storage or room and unload some of the produce without disrupting temperature conditions.
In containers, you can store vegetables that do not call for special care such as cabbage and carrots. Using this method, you can reach the required and stable humidity, temperature and air-exchange values in the storage room. In recent times, container storage has been used for potatoes, onions and garlic.
The disadvantage of container storage is the price of the containers themselves, which must be purchased for this storage type.
There are several distinct types of container storage technology:
1. Aspiration system assumes that vegetables are stored in containers in framed storehouses with the use of suction fans. The system is suitable for potatoes. beets, onions sand garlic. It allows for automating the process of storage control and monitoring humidity level, and can be supplied with heating and cooling systems depending on the type of produce and storage period.
Outside, parallel to the outer wall, a storage room wall with vertical openings is built, behind which the air preparation chamber is located. The chamber is equipped with high-pressure fans. These fans suck the waste air from the passages between the containers through the wall openings or discharge the waste air through the intake valves outside; they can also mix the waste air with the fresh air and let it back into storage. The air temperature is maintained with intake and emission valves.
In the storage, there are markings along the wall along where the containers should be placed. The space between each container should be 50cm. They are put into a pile 6-7 meters high. Above and opposite the abutting end wall, the passages between the containers are covered with metal-clad aspiration covers.
The ventilation system is fundamental and is used for drying, curing, decreasing and maintaining the temperature of produce. A refrigeration system is used at high temperatures (in May, June) or when the produce temperature needs to be decreased in a short period of time.
Aspiration system - ensures a high degree of produce safekeeping with moderate time inputs for startup.
2. Slotted wall storage technique is a type of container-based vegetable storage in framed buildings made from LSTS (light steel thin-walled structures) and sandwich panels. Just like the aspiration system, the slotted wall storage technique is suitable for storing potatoes, beets, onions and garlic and allows for automated maintenance; it can also be equipped with heating and cooling systems if needed.
For the slotted wall storage technique, storage rooms are built as high as a deck with a space of 1.5-2 meters from the outer wall of the building. Behind the wall, there is an air-ventilation chamber where equipment such as fans, intake and emission valves, servomotors, control equipment and sensors is located.
In a wall, horizontal holes are made at the height of the false bottom. Their width should be equal to the width of a container. The air flows into the storage through these holes, passing through the containers that are densely packed against the wall.
In the air-ventilation chamber itself, a false ceiling is arranged parallel to the floor at a distance of 2m. High-pressure fans are mounted into the false ceiling. They move the air from top to bottom and then it flows through horizontal doors into the storage. Above the fans on the outer wall inside the air-ventilation chamber, there are plenum valves through which fresh air flows into the storage. Waste air is removed through emission valves, which are located a bit higher on the same wall. Intake and emission valves usually have the same size and operate simultaneously.
Fresh air flows into the storage through the plenum valves, passes through the fans, and is delivered through the slots in the wall to the containers. Under pressure, the air is forced through the produce. The outgoing air is considered to be waste air and is naturally removed from the storage through the intake valves. The functioning of fans and valves is managed by a special controller and is based on the readings of high-accuracy sensors for temperature, humidity and CO2.
The main airflow goes from the bottom upwards; therefore, the produce at the bottom is better ventilated than at the top. The number of containers that can be ventilated is relatively low: 8-10 containers. Therefore, the length of the storage, as well as the length of the air-ventilation chamber, should be no less than 14-15m.
3. Pressure system is another a type of container storage for framed storehouses. Their width is a multiple of 4 and can be: 12m, 16m, 20m or 24m. The length of a storage can amount to 30m. However, the longer the storage, the worse the ventilation of all produce. The optimal length is considered to be 24m.
Like in other storage technologies, along the wall of the storage there is an air-ventilation chamber (1.5-2m in width) where equipment such as fans, intake and emission valves, servomotors, control equipment and sensors is located. The wall height between the air-ventilation chamber and storage room should be equal to the height of the container decks. Vertical holes (0.4-0.5m) are made in this wall at 80% of its height. Containers with produce are placed on either side of the holes. In the passage formed by the containers, air of the required temperature and moisture flows through the holes. Self-deploying airtubes (airbags) are mounted at the top and opposite end of the corridor so as to force the air to flow through the containers.
Fresh air passes into the storage through plenum valves; it flows from the bottom up through fans installed in the false ceiling of the air-ventilation chamber at a height of 2m and is directed into the passages from the containers. Once the air has been removed, it is considered to be waste air and is naturally removed from the storage through the intake valves. The functioning of fans and valves is managed by a special controller and is based on the readings of high-accuracy sensors for temperature, humidity and CO2.
With the help of the airbags, the pressure system provides a more intensive airflow through the produce containers. In all other aspects, the pressure system is similar to the aspiration system. The difference in cost between the two systems is explained by the airbags, which are more expensive than aspiration covers. That said, the pressure system provides a higher quality of vegetable storage.
4. EveryAir is an advanced pressure system technology. In addition to the ventilation equipment and airbags, perforated film (30cm in width) is placed in the center passage between the rows of containers. The film is located at a 8-10m distance from the wall of the air-ventilation chamber and helps the air to flow evenly. This helps ensure that all of the produce being stored is properly ventilated.
5. Dragon-M is a quick-build system of container storage for potatoes, carrots, cabbage and beets. This system can be built in either framed or arched storage buildings. The operation of the system is provided by the fans and cooling equipment, which can be mounted on the wall or floor and which is responsible for the entire technical process - from air preparation to its delivery into the storage. Depending on the configuration, the system can include heating and cooling elements, a control valve, a high-pressure fan and an air-ducting system for better airflow. Cold air descends between the containers and is then heated. Waste air is either removed through the emission valves or mixed with fresh cold outside air and brought into the fan unit.
The fan units are made from aluminum profiles. The plenum valve, along with the heating cable, is intended to provide reliable operation at low temperature conditions. The devices are supplied with axial blowers with an average air output of 75 000m3/h.
This system is less functional than other container storage systems. At the same time, it is faster and easier to erect. Plus, it is less expensive than more complex systems. This system is often used in small storages or if cold air from the outside is used for cooling produce in the winter, which helps to save on electricity. In order to maintain the required produce humidity, we recommend using the Dragon-M system along with humidifiers.

