Technology
A pressure system is used only for the container storage of vegetables and is one of today’s most effective systems. Flat-sided buildings made from LSTS (light steel thin-walled structures) and sandwich-panels are suitable for this type of storage.
Pressure system
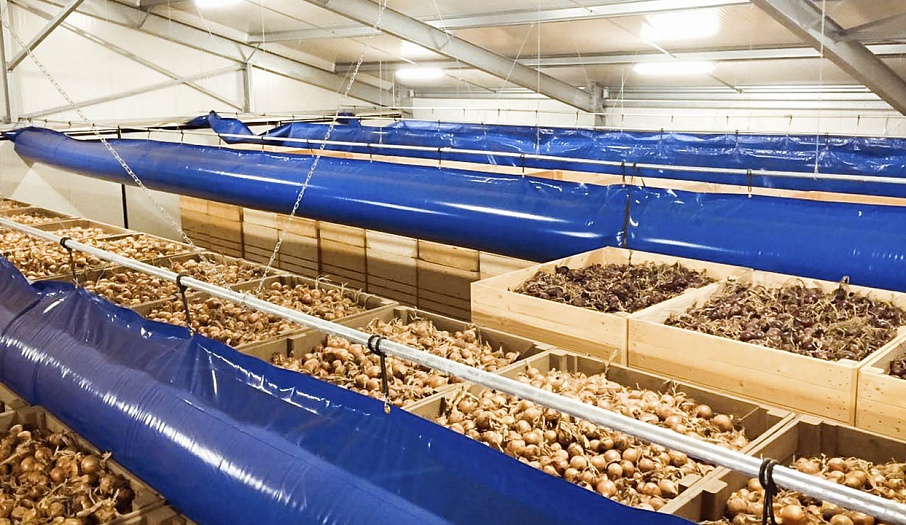
When the pressure system is used, containers are put in a certain order. Therefore, the width of storages should be a multiple of 4m: 12m, 16m, 20m or 24m. The length of a storage can be as much as 30m. However, the longer the storage, the worse the ventilation of all produce. The optimal length is considered to be 24m.
.png)
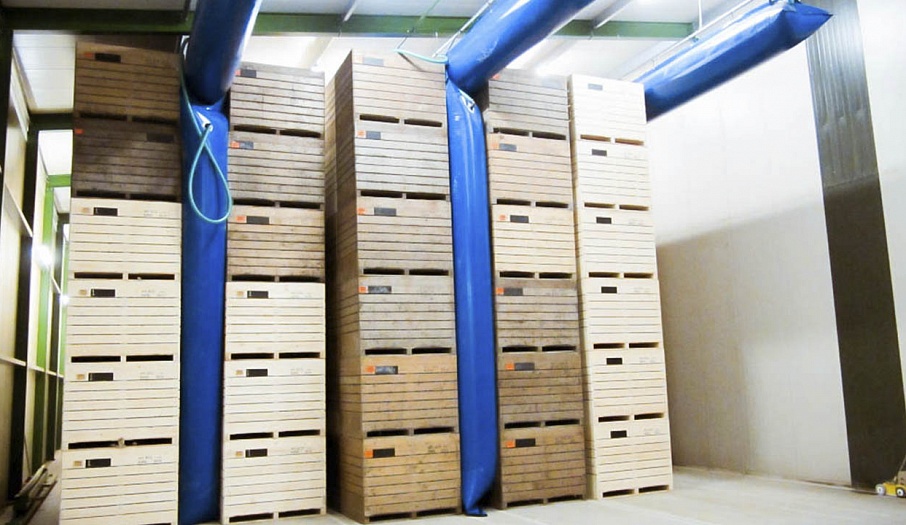
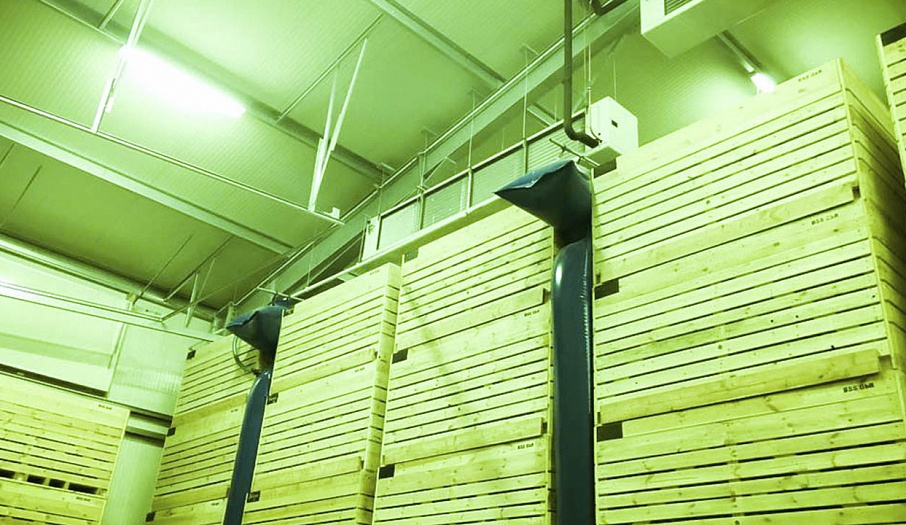
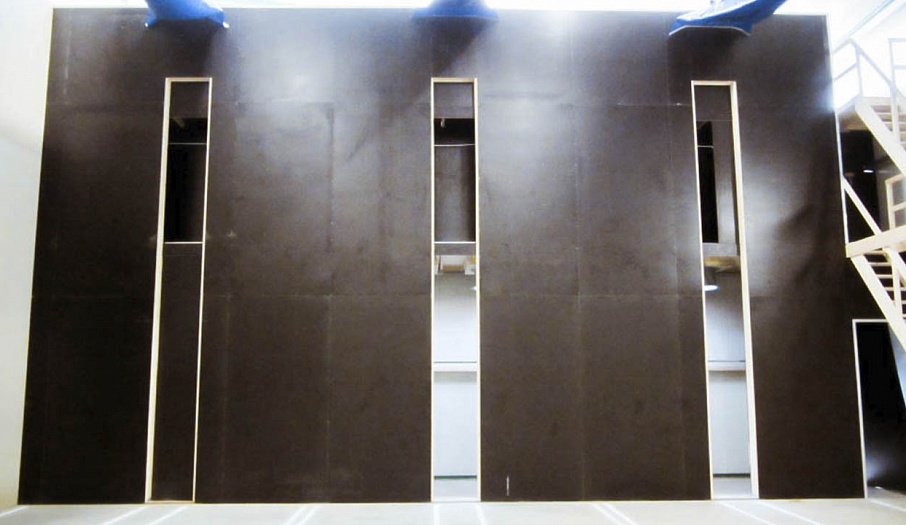
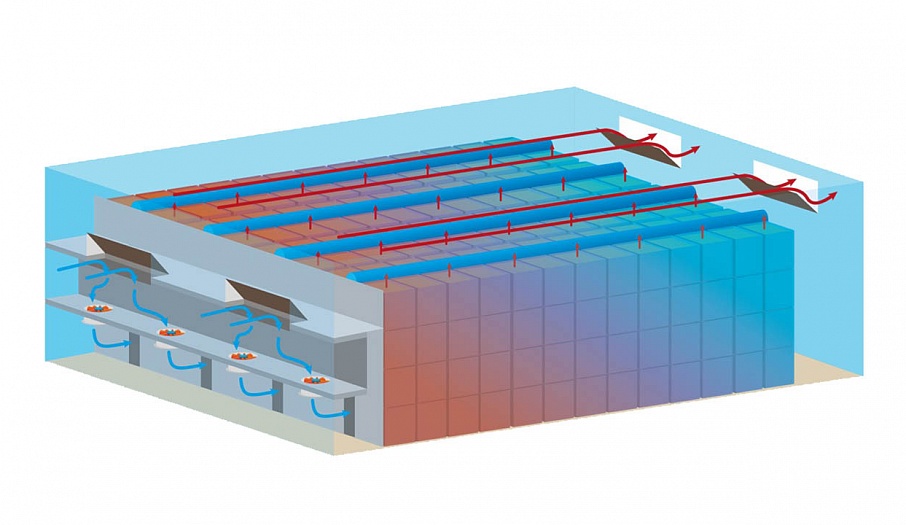
In a storage, there is an air-ventilation chamber where equipment such as fans, intake and emission valves, servomotors, control equipment and sensors is located. An air-ventilation chamber is built in a special way. At a 1.5-2m distance from the outer wall, a retaining wall is erected. Its height should be equal to the height of the containers. Vertical holes (0.4-0.5m) are made in this wall at 80% of the retaining-wall height. Produce containers are placed on either side of the holes, which results in forming a passage of containers. Because of the retaining wall, the prepared air of the required temperature and humidity flows into this passage.
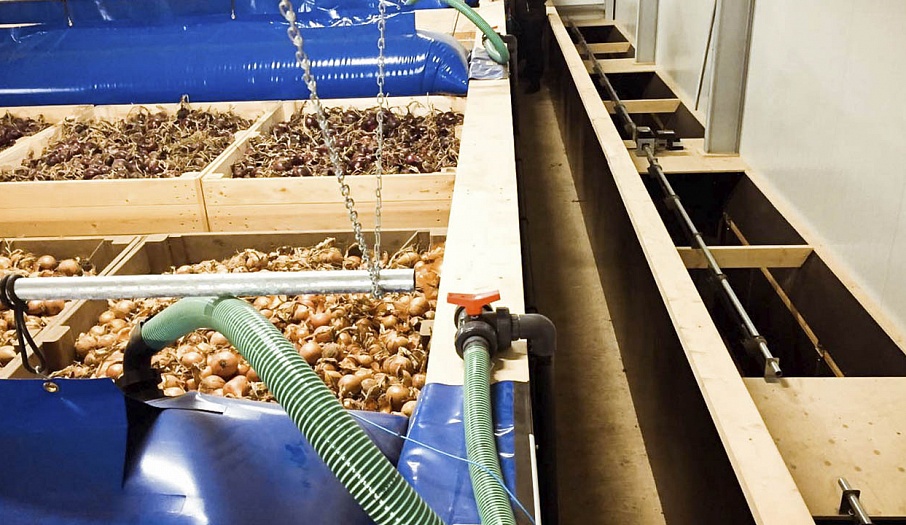
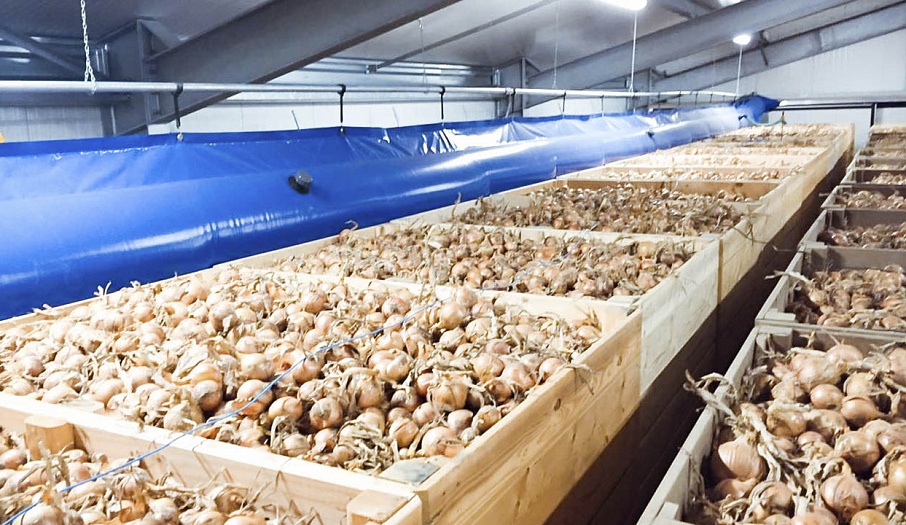
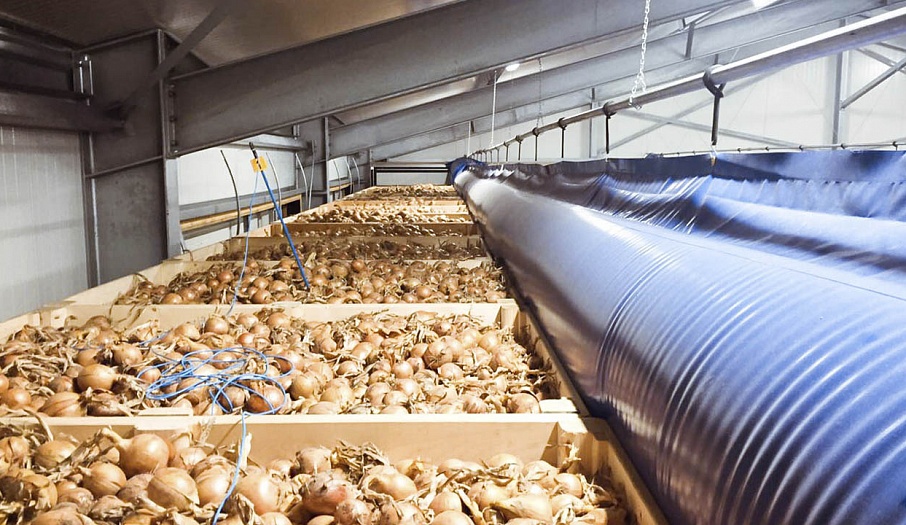
Self-deploying airtubes (airbags) are mounted at the top and opposite end of the passage so as to force the air to flow through the containers. The main airflow passes through the containers, which are placed at a distance from the retaining wall. Thus, the ventilation of these containers is better than the ventilation of those that are near the retaining wall.
In the air-ventilation chamber itself, a false ceiling is arranged at a distance of 2m. High-pressure fans are mounted into the false ceiling. They move the air from top to bottom and then it flows through vertical doors into the storage. Above the fans on the outer wall inside the air-ventilation chamber, there are plenum valves through which fresh air flows into the storage. Waste air is removed through emission valves, which are located a bit higher on the same wall. Intake and emission valves usually have the same size and operate simultaneously.
Fresh air flows into the storage through the plenum valves, passes through the fans, and is delivered into the passages formed by the containers. Under pressure, the air is forced through the produce, humidifying it and removing CO2. Once the air has been removed, it is considered to be waste air and is naturally removed from the storage through the exhaust valves.
The functioning of the ventilation system is managed by a special Croptimiz-R controller and is based on the readings of high-accuracy sensors for temperature, humidity and CO2.
Refrigeration system
A refrigeration system is used when storing at high outer temperatures (in April, May, June) or when the temperature of produce has to be decreased in a short period of time like during crop harvest or while putting produce into storage.
Artificial air cooling in a storage using a refrigeration system is designed in such a way so as to avoid impacting produce quality and minimize produce crusting and drying.
For this purpose, the system uses air coolers that have been specially designed for the storage of fruits and vegetables. They feature an enlarged heat-exchange finning surface and low air consumption, an enlarged fin pitch and “corridor” pipe pitch in the cooler housing, thereby achieving the lowest-possible “temperature drag.”
The specific arrangement of fans near the entrance to the air cooler provides the air drag into the heat exchanger of the air cooler, which decreases condensate falling onto the surface of the produce and lowers the rate of produce drying. It is extremely important that the minimum temperature drop in air coolers should be less than 6 degrees (Dt6k), that means that the boiling temperature of freon gas should be 6 degrees lower than the temperature in a chamber.
Automation
The required storage parameters are maintained with an automatic control system which was specially designed for vegetable storages.
It provides for the:
- Control of storage modes;
- Control of the refrigeration system;
- Control of the humidification system;
- Control of drying modes;
- Data collection and archiving;
- Monitoring and remote control.
The information can be automatically sent from the storage controller to a profile page or smartphone, where the user can review, organize and archive the relevant data.
Blog
Storage technology
Rectangular building conveniently
Container storage